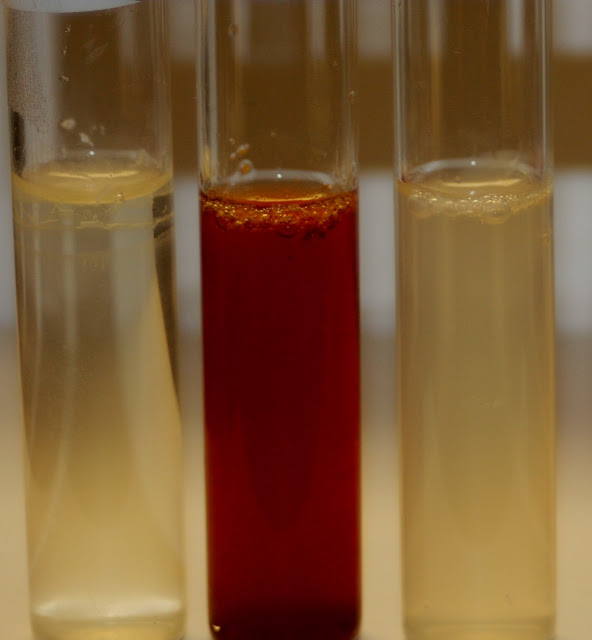
Nitrate Reduction/Nitrate Reductase Test Some bacterial species are able to reduce nitrate (NO3) to nitrite (NO2) using the enzyme nitrate reductase in an anaerobic process by using molecules other then oxygen, nitrate, as a terminal electron acceptor. To determine if a bacteria is able to reduce nitrate they are grown in a nitrate broth and a series of chemical are added to detect nitrate reduction. (A) (B) (C) Nitrate reduction test for the reduction of nitrate in nitrate media, to determine if the bacteria contains nitrate and/or nitrite reductase. Organism were incubated for 48 hr's at 37 degree's in nitrate media then reagents added. The addition of these reagents test for the presence of nitrites and the media will turn red if nitrites are present. Nitrate broths after the addition of 10 drops reagents A (sulfanilic acid in acetic acid) and B (nn-di

